Special devices
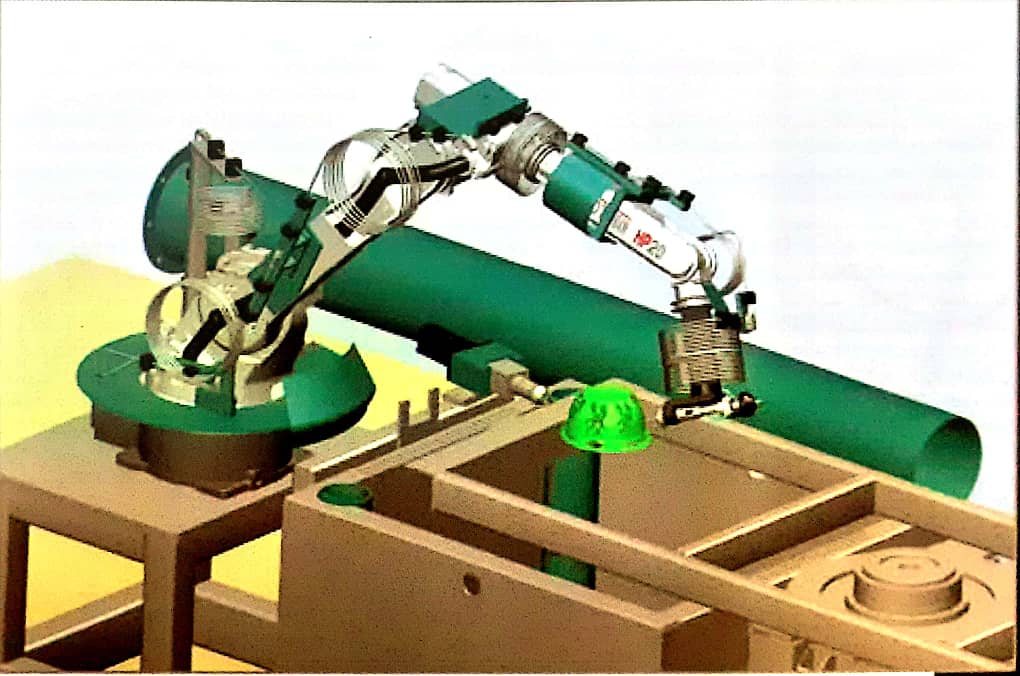
What is a robot?
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and science that includes mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science, and several other disciplines. Robotics includes the design, construction, commissioning and use of robots, as well as computer systems, control, sensor feedback and information processing. These technologies are used to upgrade machines to replace humans. Robots can be used in any situation and for any purpose, but today many of them are used in hazardous environments (such as bomb detection and deactivation), production processes, or places where humans are unable to survive. Robots can be of any shape and form, but some are designed to look like humans. This is said to be done in order to make the behaviors of these robots, which are imitated by ordinary people, more acceptable. Humanoid robots try to mimic walking, talking, recognizing, and especially anything that humans can do. Many of today's nature-inspired robots are in the realm of living creatures. The idea of creating machines that could work automatically dates back to ancient times, but no basic research has been done on the use and potential use of robots until the twentieth century. Throughout history, it has been repeatedly pointed out that one day robots will be able to mimic human behavior and do things in a similar way to humans. Today, robotics is a field of fast-growing science, as technology advances; Research, design, and construction of new robots serve several practical purposes in the domestic, industrial, and military fields. Many robots work to do dangerous jobs for people, such as working to defuse bombs, find survivors under unsustainable debris, landmines, or search for sunken ships. Robotics is also used as an educational goal in the multiple sets of science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
Morphophonemic
Robotics is derived from the word robot. The word robot itself was first coined by a Czechoslovakian writer, Karl Chapak, in a 1920 play by the Rosum Robot Factory. The word robot is derived from the Slavic word "robota", which originally means worker. The play is about a factory that produces artificial people called robots; Creatures that can be confused with humans, and this is very similar to today's modern ideas about humanoids. Carl Chapeck does not consider the word to be his own, he wrote a short letter to the Oxford English Dictionary, in which he named his brother Joseph Chapeck as the original inventor of the word.

Advantages of industrial automation:
increasing production
reduction in costs
High accuracy and speed of action

